Adapting Sustainability to Business

Condividi questo post
A Strategic Guide to Embedding ESG KPIs into the Corporate Core
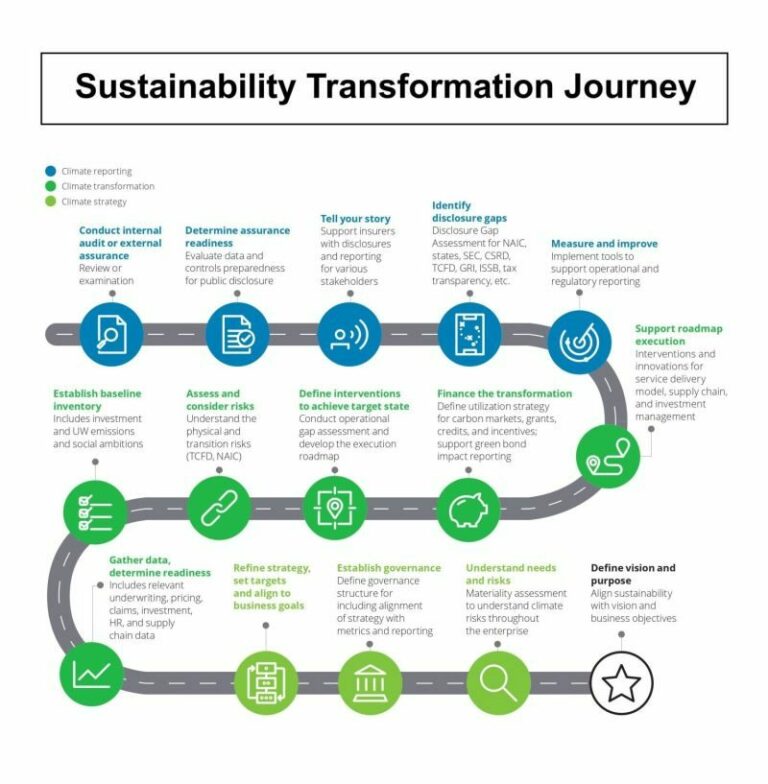
Integrating sustainability into business operations is no longer a reputational choice—it’s a strategic necessity. To gain real competitive advantage and ensure resilience and long-term value, companies must adopt a structured and systemic approach. In this article, we present a practical roadmap—suitable for any industry—to help turn ESG commitments into measurable outcomes and concrete actions.
1. Vision and Purpose: start with identity
The first step to meaningful sustainability integration is defining your corporate vision and purpose. Where does your company stand in the world? What values guide your decisions?
A clear understanding of environmental and social impacts and dependencies lays the foundation for a data-driven decision-making process, positioning sustainability as a growth enabler, not a cost.
2. Risk Assessment: anticipate vulnerabilities
Mapping physical and transition risks (climatic, regulatory, reputational, financial) is essential. Integrating these risks into long-term strategy enables operational resilience planning and readiness for shifting market conditions, regulations, and stakeholder expectations.
3. Strategic Interventions & Compliance: from plan to action
Once gaps are identified, it’s time to act. This includes:
Setting measurable ESG targets (e.g., Science-Based Targets, environmental and social KPIs)
Designing sustainability action plans
Ensuring alignment with regulations like CSRD, SFDR, EU Taxonomy, CSDDD
The goal is to bridge the gap between current performance and future sustainability objectives.
4. Investments & Financial Instruments: make sustainability tangible
ESG commitments must translate into strategic investments. Key financial levers include:
Participation in the carbon market (voluntary or regulated)
Issuing green bonds
Leveraging public incentives and sustainable finance tools
A financial perspective helps quantify the return on sustainability and ensures visibility at board level and among investors.
5. ESG Governance: bring sustainability into corporate leadership
To ensure coherence, transparency, and accountability, sustainability must be embedded in corporate governance. Having a Chief Sustainability Officer (CSO) or ESG committee at board level guarantees sustainability is part of strategic decision-making.
6. Monitoring & Reporting: what gets measured gets managed
Continuous ESG performance monitoring and reporting, aligned with the latest global standards (CSRD, TNFD, ISSB, GRI), are essential to:
Ensure transparency
Improve communication with stakeholders, investors, and clients
Enable continuous improvement
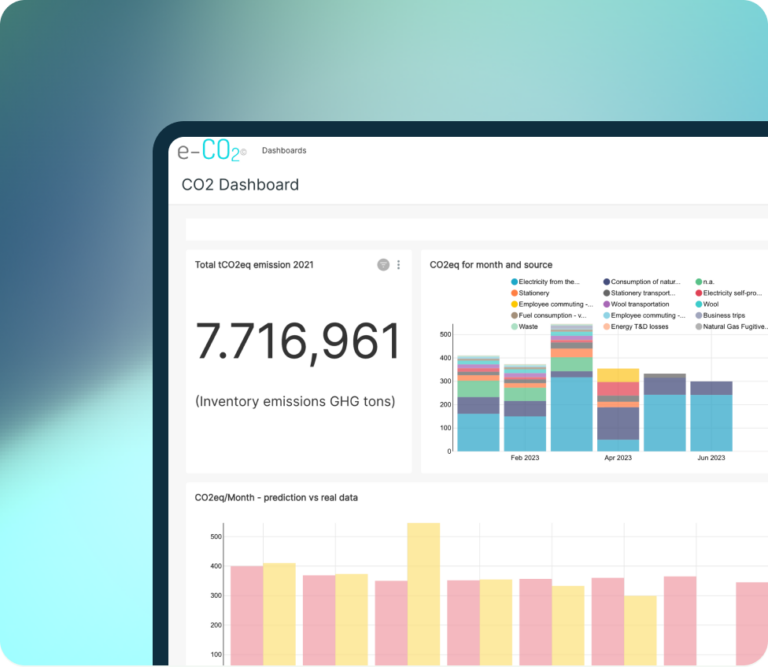
The Role of Technology: eCO₂ by ecosostenibile.eu
Without reliable, actionable data, even the best plans fall short. The eCO₂ platform by ecosostenibile.eu® empowers companies to:
Monitor every ESG KPI in real-time
Visualize performance with customizable vertical dashboards
Track progress toward net zero and regulatory compliance
Support decision-makers with clear, readable data, even for non-experts
Adapting sustainability to business means embedding it into strategy, operations, and culture. With a systemic approach—driven by data and enabled by technology—companies can turn sustainability from a perceived cost into a driver of innovation, competitiveness, and long-term value.
Christian Sansoni